Problem 68:
Consider the following “magic” 3-gon ring, filled with the numbers 1 to 6, and each line adding to nine.
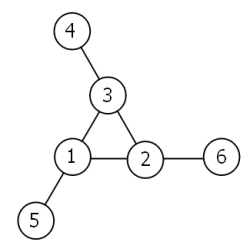
Continued reading >
Project Euler – Problem 68
Project Euler – Problem 66
Problem 66:
Consider quadratic Diophantine equations of the form:
Continued reading >
Project Euler – Problem 65
Problem 65:
The square root of 2 can be written as an infinite continued fraction.
sqrt(2) = 1+1/(2+(1/(2+1/(2+1/…))))
Continued reading >
Project Euler – Problem 64
Problem 64:
The first ten continued fraction representations of (irrational) square roots are:
Continued reading >
Project Euler – Problem 63
Problem 63:
The 5-digit number, 16807=7^5, is also a fifth power. Similarly, the 9-digit number, 134217728=8^9, is a ninth power.
How many n-digit positive integers exist which are also an nth power?
Continued reading >
Project Euler – Problem 62
Problem 62:
The cube, 41063625 (345^3), can be permuted to produce two other cubes: 56623104 (384^3) and 66430125 (405^3).
In fact, 41063625 is the smallest cube which has exactly three permutations of its digits which are also cube.
Find the smallest cube for which exactly five permutations of its digits are cube.
Continued reading >
Project Euler – Problem 61
Problem 61:
Triangle, square, pentagonal, hexagonal, heptagonal, and octagonal numbers are all figurate (polygonal) numbers and are generated by the following formulae:
Triangle P3,n=n(n+1)/2 1, 3, 6, 10, 15, ... Square P4,n=n2 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, ... Pentagonal P5,n=n(3n-1)/2 1, 5, 12, 22, 35, ... Hexagonal P6,n=n(2n-1) 1, 6, 15, 28, 45, ... Heptagonal P7,n=n(5n-3)/2 1, 7, 18, 34, 55, ... Octagonal P8,n=n(3n-2) 1, 8, 21, 40, 65, ...
The ordered set of three 4-digit numbers: 8128, 2882, 8281, has three interesting properties.
The set is cyclic, in that the last two digits of each number is the first two digits of the next number (including the last number with the first).
Continued reading >
Project Euler – Problem 60
Problem 60:
The primes 3, 7, 109, and 673, are quite remarkable. By taking any two primes and concatenating them in any order the result will always be prime.
Continued reading >
Project Euler – Problem 59
Problem 59:
The encryption key consists of three lower case characters. Using cipher1.txt, a file containing the encrypted ASCII codes, and the knowledge that the plain text must contain common English words, decrypt the message and find the sum of the ASCII values in the original text.
Note that the key is repeated cyclically throughout the message utilizing XOR.
Continued reading >
Project Euler – Problem 58
Problem 58:
Starting with 1 and spiralling anticlockwise in the following way, a square spiral with side length 7 is formed.
37 36 35 34 33 32 31 38 17 16 15 14 13 30 39 18 5 4 3 12 29 40 19 6 1 2 11 28 41 20 7 8 9 10 27 42 21 22 23 24 25 26 43 44 45 46 47 48 49
Continued reading >